Primary Rocks: Types & Characteristics
Primary rocks, also known as igneous rocks, are the fundamental building blocks of the Earth’s crust. They offer crucial insights into the planet’s geological history, making them essential for competitive exam preparations such as the UPSC.
This article provides an in-depth exploration of the characteristics and different types of primary rocks, equipping UPSC aspirants with valuable knowledge for their studies.
| Property | Description |
| Origin | Magma/Lava |
| Texture | Coarse/Fine |
| Minerals | Silicates |
| Color | Varied |
| Density | High |
| Location | Earth’s Crust |
| Significance | Geological Insight |
What are Primary Rocks?
Primary rocks, also known as igneous rocks, are one of the three main types of rocks found on Earth, alongside sedimentary and metamorphic rocks. They are called “primary” because they are the first to form in the Earth’s crust. These rocks are created through the solidification and crystallization of molten material, either magma (when still beneath the Earth’s surface) or lava (when erupted onto the surface).
How Primary Rocks are Formed?
The formation of primary rock occurs in the following way:
- Magma Formation: Magma is generated deep within the Earth’s mantle through processes like partial melting of rocks. It is composed of molten minerals and gases.
- Magma Movement: Magma, being less dense than the surrounding rock, rises towards the Earth’s surface. It can remain below the surface, forming intrusive igneous rocks, or it can erupt onto the surface, creating extrusive igneous rocks.
- Solidification and Crystallization: As magma cools, it solidifies and crystallizes, leading to the formation of primary rocks. The rate of cooling determines the size of the crystals in the rock.
Types of Primary Rocks
There are several types of primary rocks, having their own distinct characteristics and mineral composition:
- Granite
- Basalt
- Diorite,
- Gabbro
- Peridotite
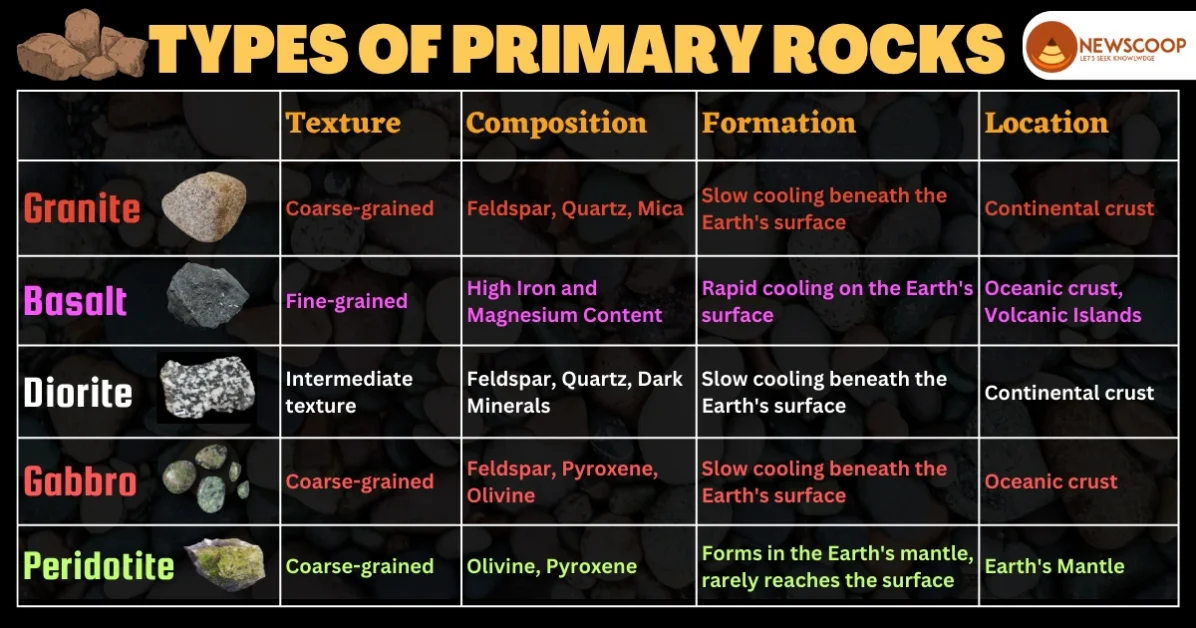
1. Granite
- Coarse-grained texture
- Predominantly composed of feldspar, quartz, and mica
- Light-colored
- Forms through the slow cooling of magma beneath the Earth’s surface
- Commonly found in continental crust
2. Basalt
- Fine-grained texture
- Predominantly composed of high iron and magnesium content
- Dark-colored
- Forms from the rapid cooling of lava on the Earth’s surface
- Abundant in oceanic crust, often found in volcanic islands
3. Diorite
- Intermediate texture, between granite and basalt
- Speckled appearance
- Commonly found in continental crust
- Forms through the slow cooling of magma beneath the Earth’s surface
4. Gabbro
- Intrusive equivalent of basalt
- Composed of larger crystals due to slower cooling beneath the surface
- Dark-colored
- Commonly found in the oceanic crust
5. Peridotite
- Ultramafic composition rich in olivine and pyroxene
- Typically found in the Earth’s mantle
- Rarely reaches the Earth’s surface
Characteristics of Primary Rocks
Primary rocks possess certain key characteristics:
- Texture: They have interlocking crystal structures due to the slow cooling process beneath the Earth’s surface, resulting in a coarse-grained texture. Rapid cooling on the surface creates fine-grained textures.
- Mineral Composition: These rocks are primarily composed of silicate minerals, including quartz, feldspar, mica, and various dark-colored minerals like pyroxene and amphibole.
- Color: The color of these rocks varies widely depending on the mineral content. Rocks with high silica content tend to be lighter, while those rich in iron and magnesium are darker.
- Density: They generally have higher density compared to sedimentary and metamorphic rocks, mainly due to the presence of dense minerals like olivine and pyroxene.
Conclusion
Understanding primary rocks is fundamental for comprehending the Earth’s geological processes. For UPSC aspirants, a solid grasp of these rocks provides a strong foundation for answering questions related to geology in the exam. Remember to revise and practice with sample questions to consolidate your knowledge. Good luck with your preparations!
Thank You!
FAQs
Why igneous rocks are called primary rocks?
Igneous rocks are called primary rocks because they form directly from the solidification of molten material (magma or lava), making them the first rocks to originate in Earth’s geological processes.
Which rocks are called primary rocks?
Primary rocks, also known as igneous rocks, are the first type of rocks formed in the Earth’s crust.

