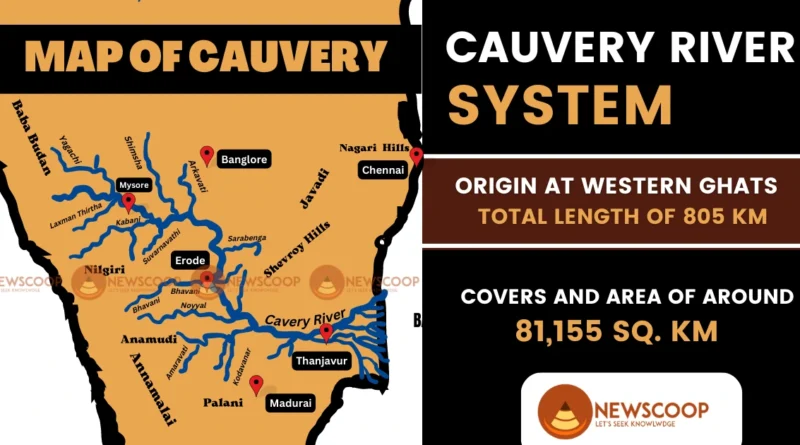
Cauvery River: Tributaries & Map of Kaveri in India
The Cauvery River, often referred to as the “Ganges of the South,” is one of the most significant rivers in India. Originating in the Western Ghats of Karnataka and flowing through the states of Tamil Nadu and Puducherry, the river has played a crucial role in shaping the ecological, socioeconomic, and cultural landscapes of the region.
This article explores the importance of the Cauvery River, its physical features, historical significance, current challenges, and its impact on the livelihoods of millions of people.
| River | Cauvery |
| Origin | Talakaveri in the Western Ghats, Karnataka |
| States | Karnataka, Tamil Nadu, and Puducherry |
| Length | Approximately 805 kilometers |
| Basin Area | Around 81,155 square kilometers |
| Tributaries | Kabini, Hemavati, Shimsha, Arkavathi, and Amaravati rivers |
| Waterfalls | Shivanasamudra Falls |
| Delta | Cauvery Delta (Rice Bowl of Tamil Nadu) |
| Reservoirs | Krishna Raja Sagara, Kabini, Mettur, and Stanley Reservoir |
Geographical Features of the Cauvery/Kaveri River System
The Cauvery River system encompasses various geographical features that contribute to its overall significance and ecological diversity. Here are some key aspects of the Cauvery River’s geography:
- Originates from Talakaveri in the Western Ghats, Karnataka.
- Flows through Karnataka, Tamil Nadu, and Puducherry.
- Covers a total length of approximately 805 kilometers.
- The river basin spans an area of around 81,155 square kilometers.
- Fed by tributaries including the Kabini, Hemavati, Shimsha, Arkavathi, and Amaravati rivers.
- Features captivating waterfalls like Shivanasamudra Falls.
- Forms the fertile Cauvery delta, known as the “Rice Bowl of Tamil Nadu.“
- Numerous reservoirs and dams were constructed along the river, such as Krishna Raja Sagara, Kabini, Mettur, and Stanley Reservoir.
- Supports diverse ecosystems and a wide range of wildlife, including elephants, tigers, crocodiles, and various bird species.
Origin & Source
The Cauvery River originates from Talakaveri, a peak in the Western Ghats of Karnataka. The source of the river is a small spring known as the Cauvery Kundike. Situated at an altitude of around 1,262 meters, Talakaveri is located in the Coorg district of Karnataka, India. This pristine natural spring marks the starting point of the Cauvery River, where it begins its journey toward the plains.
Map of Cauvery River

What is the Course of the Cauvery River?
The Cauvery River flows through the states of Karnataka, Tamil Nadu, and Puducherry, covering a total distance of approximately 800 kilometers. As it follows its course, the river meanders through diverse landscapes, including mountains, plateaus, and the fertile Cauvery delta.
After winding its way through the land, the Cauvery River finally reaches its destination as it empties into the Bay of Bengal near the town of Poompuhar in Tamil Nadu. This estuarine area serves as the final resting place for the river, where its waters merge with the vast expanse of the ocean.
Along its course, the river plays a vital role in providing water for irrigation, drinking, and other domestic uses, supporting the livelihoods of millions of people who rely on its waters for various purposes.
Major Cities along its Course
Here is a list of major cities along the course of the Cauvery River:
- Mysuru
- Srirangapatna
- Shivanasamudra
- Sivasamudram
- Mettur
- Erode
- Karur
- Thanjavur
- Kumbakonam
Tributaries of the Cauvery River
- Hemavati River
- Shimsha River
- Arkavathy River
- Lakshmanathirtha River
- Kabini River
- Suvarnavathi River
- Noyyal River
- Amaravati River
- Bhavani River
| Left Bank Tributaries | Right Bank Tributaries |
|---|---|
| Harangi | Lakshmana Tirtha |
| Hemavati | Kabini |
| Shimsha | Suvarnavati |
| Arkavati | Bhavani |
| Noyil | |
| Amaravati |

Dams on the Cauvery River
- Krishna Raja Sagara Dam
- Mettur Dam
- Kabini Dam
- Hemavati Dam
- Harangi Dam
- Bhavanisagar Dam
- Amaravati Dam
- Banasura Sagar Dam
- Moyar Dam
- Solaiyar Dam
Historical Significance of the Cauvery River
The historical significance of the Cauvery River holds immense importance in the cultural heritage and development of South India. With references found in ancient scriptures and literary works, the river has played a pivotal role in shaping the region’s civilization and cultural identity.
The Cauvery River is mentioned in the Sangam literature, which dates back over two thousand years. These ancient Tamil texts celebrate the river’s beauty, purity, and life-giving properties, often personifying it as a revered goddess known as “Kaveri Amman” or “Kaveri Thayar.“
Throughout history, the river basin has been a cradle of civilization, fostering the growth of ancient kingdoms. The Chola dynasty, one of South India’s most influential dynasties, flourished along the river’s banks. They developed sophisticated irrigation systems to harness the river’s waters for agriculture, leading to remarkable advancements in farming techniques and trade.
Moreover, the river has witnessed significant historical events. Srirangam, an island in the Cauvery River, is home to the renowned Sri Ranganathaswamy Temple, a major pilgrimage site and cultural center. The temple has stood for centuries, attracting devotees from all over the country.
However, the river has not been without conflicts. Disputes over the sharing of Kaveri River waters have arisen between kingdoms and, later, between states. The issue of water sharing between Karnataka and Tamil Nadu has resulted in legal battles and tensions, underscoring the river’s historical and contemporary significance.
The Cauvery River’s historical significance extends beyond its immediate vicinity. It facilitated trade and cultural exchange, with ports and towns emerging along its course. The river served as a vital waterway for transportation, enabling the movement of goods, ideas, and people across the region.
Also Read: Krishna River System
Ecological Importance
The Cauvery River basin is a unique ecological hotspot, supporting a rich biodiversity and diverse ecosystems. The river and its tributaries provide a lifeline to numerous flora and fauna species, including endangered and endemic ones. The forests surrounding the river are home to a wide range of wildlife, including elephants, tigers, and various species of birds.
Moreover, the river plays a crucial role in replenishing groundwater resources in the region. It recharges the aquifers, ensuring a steady supply of water for drinking, irrigation, and industrial purposes. The river’s flow also helps maintain the health of wetlands and contributes to the overall ecological balance.
Conclusion
In conclusion, the Cauvery River system is a significant water resource in South India. It originates from Talakaveri in the Western Ghats and flows through Karnataka, Tamil Nadu, and Puducherry. The river supports agriculture, provides water for various purposes, and has historical and cultural importance.
Further, it is fed by important tributaries from both the left and right banks. The Kaveri River system is home to major cities and towns, contributing to the region’s development. Conservation and management of the river’s resources are crucial for its sustainability and the well-being of the communities dependent on it.
Thank You!
FAQs
What is the origin of the Cauvery River?
The Cauvery River originates from the Brahmagiri Hills in the Western Ghats of Karnataka, India. It specifically originates from a place called Talakaveri, which is located at an elevation of about 1,276 meters (4,186 feet) above sea level.
What is the total length of the Cauvery River?
The total length of the Cauvery River is approximately 805 kilometers (497 miles). It flows through the states of Karnataka, Tamil Nadu, and Puducherry in South India.
Cauvery River flows through which states?
The Cauvery River flows through the states of Karnataka, and Tamil Nadu.
What are the major tributaries of the Cauvery River?
The major tributaries of the Cauvery River are:
Hemavati River
Arkavati River
Kabini River
Bhavani River
Amaravathi River
Noyyal River
Related Links: