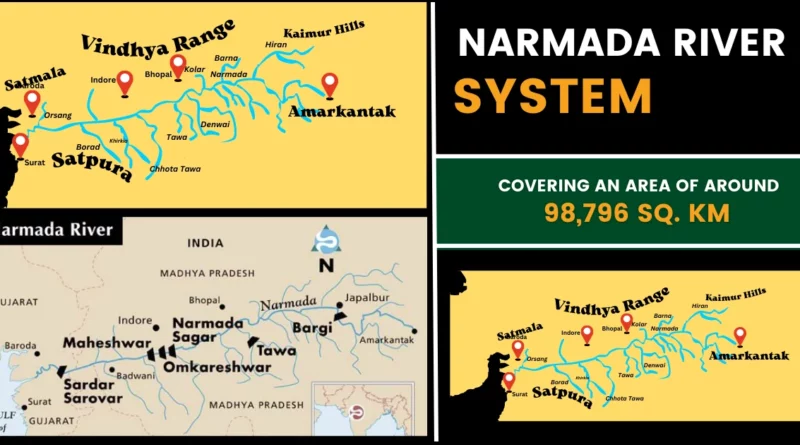
Narmada River System: Map | Tributaries & Dams
The Narmada River, known as the lifeline of Central India, holds great historical, cultural, and ecological significance. Flowing through the states of Madhya Pradesh, Gujarat, and Maharashtra, this sacred river has nurtured civilizations for centuries and continues to provide numerous benefits to the region.
Understanding the importance of the Narmada River is essential for UPSC exam aspirants, as it encompasses various aspects of geography, history, and environmental studies. This article will explore the Narmada River, covering its origin, course, tributaries, dams, religious significance, and ecological importance.
| River | Narmada River |
| Length | Approx. 1,312 km |
| Origin | Amarkantak plateau in Madhya Pradesh |
| States | Madhya Pradesh, Maharashtra, Gujarat |
| Tributaries | Tawa, Hiran, Barna, Shakkar, Dudhi, Tendoni, Burhner, and others |
| Major Dams | Sardar Sarovar Dam, Indira Sagar Dam, Bargi Dam, and others |
| Mouth | Gulf of Khambhat (Arabian Sea) |
Narmada River
The Narmada River, popularly referred to as the Reva, holds the distinction of being India’s fifth-longest river and the longest west-flowing river in the country. It is also recognized as the largest flowing river within the state it traverses. Moreover, the Narmada River flows through a rift valley, carving its way between the Satpura and Vindhya mountain ranges, making it one of the significant rivers in India that follows this geological formation.
Origin & Course
- The Narmada River originates in the Amarkantak Plateau of the Maikala range in the Anuppur District of eastern Madhya Pradesh.
- It begins at an elevation of 1,057 meters above mean sea level.
- The river traverses a distance of 1,312 km before it merges into the Gulf of Cambay in the Arabian Sea near Bharuch, Gujarat.
- The first 1,079 km of the Narmada River is in Madhya Pradesh.
- It then forms the boundary between Madhya Pradesh and Maharashtra for 35 km.
- Next, it forms the boundary between Maharashtra and Gujarat for a length of 39 km.
- The last stretch of 159 km of the Narmada River lies in Gujarat.
River Basin
- The Narmada River basin encompasses an area of 98,796 sq. km.
- It is bounded on the north by the Vindhyas, on the east by the Maikala range, on the south by the Satpuras, and on the west by the Arabian Sea.
- Most of the Narmada River basin is less than 500 meters above mean sea level.
- Only a small area around Panchmarhi is at an elevation of more than 1,000 meters above mean sea level.
Drainage Area
The Narmada River basin is spread across three states:
- Madhya Pradesh: 85,859 sq. km.
- Maharashtra: 1,538 sq. km.
- Gujarat: 11,399 sq. km.
Waterfalls on the Narmada River
The Narmada River, located in central India, is known for its scenic beauty and is home to several waterfalls. Here are some of the prominent waterfalls along the Narmada River:
| Waterfall Name | Location |
|---|---|
| Dhuan Dhar Falls | Jabalpur, Madhya Pradesh |
| Mandhar Waterfall | Jabalpur, Madhya Pradesh |
| Dardi Waterfall | Jabalpur, Madhya Pradesh |
| Sahastradhara Falls | Maheshwar, Madhya Pradesh |
| Bhedaghat Falls | Jabalpur, Madhya Pradesh |
| Kapil Dhara Falls | Amarkantak, Madhya Pradesh |
Map of Narmada River
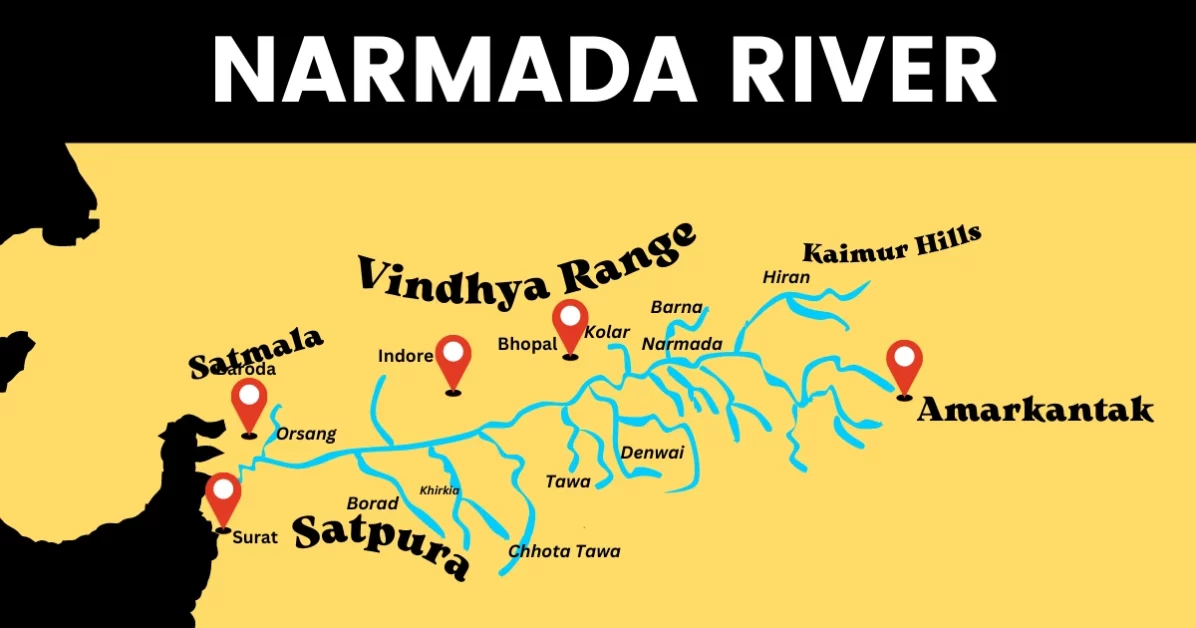
Tributaries of Narmada River
Following are the left and right bank tributaries of the Narmada River:
| Right Bank Tributaries | Left Bank Tributaries |
|---|---|
| The Barna River | Buehner River |
| Hiran River | Banjar River |
| Tendoni River | Sher River |
| Choral River | Shakkar River |
| Kolar River | Dudhi River |
| Man River | Tawa River |
| Uri River | Ganjal River |
| Hatni River | Chhota Tawa River |
| Orsang River | Kaveri River |
| Kundi River | |
| Goi River | |
| Karjan River |
Dams on the Narmada River
Here are some of the prominent dams constructed on the Narmada River:
| Dam | Location | Purpose | Height (m) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Sardar Sarovar Dam | Navagam, Gujarat | Irrigation, Water Supply, Hydroelectric Power | 163 |
| Indira Sagar Dam | Narmada Nagar, MP | Irrigation, Hydroelectric Power | 92 |
| Omkareshwar Dam | Omkareshwar, MP | Hydroelectric Power, Irrigation | 65 |
| Bargi Dam | Jabalpur, MP | Irrigation, Hydroelectric Power | 69 |
| Jobat Dam | Jobat, MP | Irrigation | 35 |
| Maheshwar Dam | Maheshwar, MP | Hydroelectric Power, Irrigation | 47 |
Religious & Cultural Significance
- Holy River: The Narmada River holds immense religious significance in Hindu mythology and is considered one of the seven sacred rivers in India.
- Pilgrimage: The Narmada River is associated with numerous pilgrimage sites, including the Amarkantak, Omkareshwar, Maheshwar, and the Narmada Sagar dams, which attract devotees and tourists.
- Ritual Bathing: Taking a dip in the Narmada River is believed to cleanse sins and purify the soul according to Hindu beliefs.
- Festivals: The Narmada Jayanti (birth anniversary of the river) and Narmada Parikrama (circumambulation of the river) is celebrated with great enthusiasm by devotees.
Read: Major Rivers of India
Conclusion
In conclusion, the Narmada River is a significant river in central India, known for its religious, cultural, ecological, and historical importance. Considered one of the sacred rivers in Hindu mythology, it holds a special place in the hearts of devotees who believe in its purifying powers. The river is associated with pilgrimage sites and festivals that attract devotees and tourists alike.
Beyond its religious and cultural significance, the Narmada River plays a crucial role in supporting diverse ecosystems and wildlife in its basin. Conservation efforts are aimed at preserving the river’s biodiversity and protecting endangered species.
Overall, the Narmada River stands as a symbol of spiritual devotion, ecological richness, and historical legacy, weaving together the fabric of India’s diverse tapestry.
Thank You!
FAQs
What is the length of the Narmada River?
The Narmada River is approximately 1,312 kilometers long, making it one of the longest rivers in India.
Where does the Narmada River originate?
The Narmada River originates from the Amarkantak plateau in Madhya Pradesh, near the village of Amarkantak.
What is the significance of the Narmada River in Indian culture?
The Narmada River holds immense cultural and religious significance in India. It is considered one of the seven holy rivers and is associated with various myths, legends, and pilgrimage sites along its course.
Related Links: