Elephants are magnificent creatures that need our help to thrive. In India, the government has set up special places called Elephant Reserves to keep them safe. These reserves are like homes for elephants, where they can live happily in their natural habitats.
In this article, we will learn about some of these Elephant Reserves in India and why they are so important. This information will be useful for aspirants studying for the UPSC exams.
India’s 33rd Elephant Reserve
What is an Elephant Reserve?
An Elephant Reserve is a designated area established to protect and preserve elephants and their habitats. It provides a safe and secure environment for elephants to live in, ensuring their survival and well-being. Further, these reserves are crucial for maintaining healthy elephant populations and the ecological balance of their ecosystems. Through conservation efforts and management strategies, Elephant Reserves aim to safeguard these magnificent creatures for future generations.
Objectives of Elephant Reserves
The primary objectives of Elephant Reserves are:
- Conservation of elephant populations.
- Preservation of elephant habitats.
- Mitigation of human-elephant conflicts.
- Biodiversity conservation.
- Socio-economic development for local communities.
- Management of elephant corridors.
- Scientific research and monitoring.
- Promotion of eco-tourism.
First Elephant Reserve in India
Elephant conservation efforts in India have a rich history that dates back several decades. In 1992, the Government of India established Project Elephant as a Centrally Sponsored Scheme. The primary goals of this initiative were to protect elephants, their habitats, and migration routes, resolve human-animal conflicts, and ensure the well-being of elephants in captivity.
As part of Project Elephant, the Singhbhum Elephant Reserve was created in 2001, marking the country’s first Elephant Reserve. Spanning an expansive area of 13,440 square kilometers, the reserve became a crucial stronghold for elephants. It served as a model for future Elephant Reserves in the country, laying the foundation for comprehensive elephant conservation efforts.
Governing Body
The governing body responsible for overseeing and managing Elephant Reserves in India is the Ministry of Environment, Forest and Climate Change(MoEFCC). This ministry formulates policies, guidelines, and regulations related to the conservation and protection of elephants and their habitats.
Moreover, it provides financial and technical support to the major elephant range states and coordinates efforts to ensure the effective management of Elephant Reserves.
Nodal Agency
The nodal agency, which is Project Elephant, is responsible for the implementation and coordination of activities within Elephant Reserves. It acts as a bridge between the governing body and the on-ground stakeholders.
Further, it works closely with state forest departments, wildlife authorities, and local communities to implement conservation measures, manage habitats, address human-elephant conflicts, conduct scientific research, and ensure the welfare of captive elephants. The nodal agency is actively involved in day-to-day operations and on-ground conservation activities within the Elephant Reserves.
Elephant Reserves on India Map
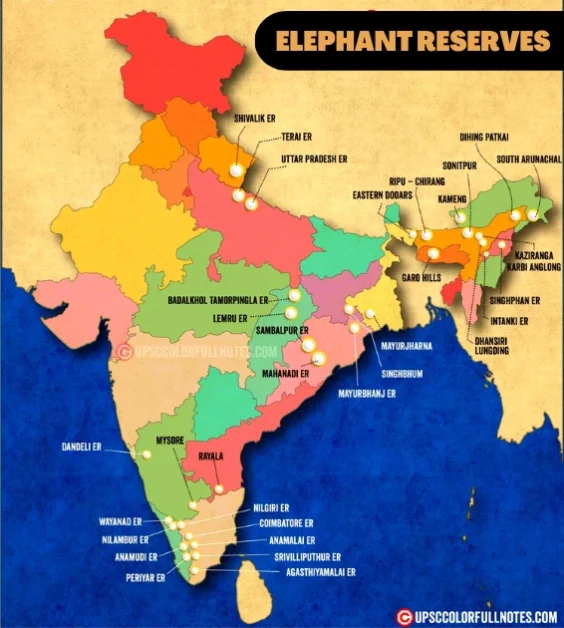
Number of Elephant Reserves in India
India is home to the largest population of wild Asian elephants, with around 27,312 elephants. They reside across 14 states, covering approximately 80,000 square kilometers of forested areas. The elephants’ home ranges can vary from 250 to over 3,500 square kilometers, depending on the landscape. Preserving these habitats is crucial for the conservation of this iconic species.
As of 2023, there are a total of 33 officially recognized Elephant Reserves in India. These reserves are distributed across various states, ensuring the conservation of elephant populations in different regions.
The following table shows all elephant reserves in India with their location and area cover:
| S. No. | Elephant Reserve | State | Date of Notification | Total Area (Sq. Km) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Singhbhum ER | Jharkhand | 26.09.2001 | 4,530 |
| 2 | Garo Hills ER | Meghalaya | 31.10.2001 | 3,500 |
| 3 | Nilambur ER | Kerala | 02.04.2002 | 1,419 |
| 4 | Anamudi ER | Kerala | 02.04.2002 | 3,728 |
| 5 | Periyar | Kerala | 02.04.2002 | 3,742 |
| 6 | Wayanad ER | Kerala | 02.04.2002 | 1,200 |
| 7 | Sambalpur ER | Odisha | 27.03.2002 | 427 |
| 8 | Mahanadi ER | Odisha | 20.07.2002 | 1,038 |
| 9 | Mayurjharna ER | West Bengal | 24.10.2002 | 414 |
| 10 | Mysore ER | Karnataka | 25.11.2002 | 6,724 (Largest) |
| 11 | Shivalik ER | Uttarakhand | 28.10.2002 | 5,405 |
| 12 | Dandeli ER | Karnataka | 26.03.2015 | 2,321 |
| 13 | Intanki ER | Nagaland | 28.02.2005 | 202 |
| 14 | Sonitpur ER | Assam | 06.03.2003 | 1,420 |
| 15 | Chirang-Ripu ER | Assam | 07.03.2003 | 2,600 |
| 16 | Dihing-Patkai ER | Assam | 17.04.2003 | 937 |
| 17 | Kaziranga – Karbi Anglong ER | Assam | 17.04.2003 | 3,270 |
| 18 | Nilgiri ER | Tamil Nadu | 19.09.2003 | 4,663 |
| 19 | Coimbatore ER | Tamil Nadu | 19.09.2003 | 566 |
| 20 | Anamalai ER | Tamil Nadu | 19.09.2003 | 1,457 |
| 21 | Srivilliputtur ER | Tamil Nadu | 19.09.2003 | 1,249 |
| 22 | Kameng ER | Arunachal Pradesh | 19.06.2002 | 1,892 |
| 23 | Mayurbhanj ER | Odisha | 29.09.2001 | 3,214 |
| 24 | Rayala ER | Andhra Pradesh | 09.12.2003 | 766 |
| 25 | Badalkhol-Tamorpingla ER | Chhattisgarh | 15.09.2011 | 1,048.30 |
| 26 | Uttar Pradesh ER | Uttar Pradesh | 09.09.2009 | 744 |
| 27 | Dhansiri-Lungding ER | Assam | 19.04.2003 | 2,740 |
| 28 | South Arunachal ER | Arunachal Pradesh | 29.02.2008 | 1,957.50 |
| 29 | Eastern Dooars ER | West Bengal | 28.8.2002 | 978 |
| 30 | Singphan ER | Nagaland | 16.08.2018 | 23.57 |
| 31 | Lemru ER | Chhattisgarh | 2022 | 450 |
| 32 | Agsthyamalai ER | Tamil Nadu | 12.08.2022 | 1,197.48 |
| 33 | Terai ER | Uttar Pradesh | 2022 | 3,049 |
Overview of Elephant
The scientific name for the Asian elephant is Elephas maximus. This name is derived from the Greek word “elephas,” which means “ivory” or “elephant.” The term “Maximus” is of Latin origin and translates to “greatest” or “largest,” referring to the size of the species. Elephas maximus is the only living species in the Elephas genus.
Species of Elephant
Elephants, magnificent and majestic creatures, are classified into three distinct species:
- African bush elephants (Loxodonta africana)
- African forest elephants (Loxodonta cyclotis)
- Asian elephants (Elephas Maximus)
1. African Bush Elephants
African bush elephants are the largest land animals on Earth. They have distinctively large ears and tusks, and their habitats primarily include savannahs, grasslands, and open woodlands across sub-Saharan Africa.
- Also called African Savannah Elephants
- IUCN Red List: Endangered
- CITES: Appendix II
2. African Forest Elephants
African forest elephants, on the other hand, are smaller in size and have more rounded ears compared to their bush counterparts. They inhabit the dense rainforests of Central and West Africa, where they play a vital role in seed dispersal and forest regeneration.
- The global population of African elephants is estimated to be around 400,000.
- IUCN Red List: Critically Endangered
- CITES: Appendix II
3. Asian Elephants
Asian elephants, found in countries like India, Sri Lanka, Thailand, and Myanmar, are characterized by their relatively smaller size and prominent domed heads. They have long trunks, large ears, and tusks, and they primarily inhabit forests and grasslands in Asia.
- Asian elephants are classified into three subspecies: Indian, Sumatran, and Sri Lankan.
- The Indian subspecies has the largest range and constitutes the majority of the Asian elephant population.
- The global population of Asian elephants ranges from 20,000 to 40,000.
- IUCN Red List: Endangered
- The Wildlife (Protection) Act of 1972: Protected under Schedule I
- CITES: listed under Appendix I, which prohibits international trade in their specimens.
Also Read: Important IUCN Species
Importance of Elephant Reserves
- Elephant Reserves protect critical habitats for wild Asian elephants, ensuring their survival and conservation.
- They serve as important corridors for elephant movement, allowing for genetic exchange and maintaining population connectivity.
- Elephant Reserves help mitigate human-elephant conflicts by providing designated spaces for elephants to roam and reducing encounters with human settlements.
- They support the overall biodiversity of ecosystems by conserving not only elephants but also a wide range of flora and fauna.
- They play a vital role in research and monitoring programs, providing valuable data for scientific studies and conservation initiatives.
- They support the conservation of endangered species that coexist with elephants in their habitats.
- Elephant Reserves contribute to climate change mitigation by protecting forest ecosystems, which act as carbon sinks and help regulate the climate.
- They serve as living laboratories for studying elephant behavior, ecology, and social dynamics, contributing to our understanding of these magnificent creatures.
Challenges & Future Perspectives
Habitat Fragmentation and Loss: One of the significant challenges for elephant conservation is habitat fragmentation and loss due to human activities such as deforestation, urbanization, and infrastructure development. This disrupts elephant corridors and restricts their movement, leading to increased human-elephant conflicts.
Climate Change Impacts on Elephant Habitats: Climate change poses a threat to elephant habitats by altering vegetation patterns, water availability, and food sources. Rising temperatures and changing rainfall patterns can further exacerbate the challenges faced by elephants, affecting their survival and migration patterns.
Policy Reforms and Collaborative Approaches for Conservation: To address these challenges, it is crucial to have effective policy reforms that prioritize elephant conservation. Collaboration between governments, local communities, NGOs, and stakeholders is essential to ensure sustainable and inclusive conservation efforts.
Conservation Initiatives in Elephant Reserves
Anti-Poaching Measures and Wildlife Protection: Elephant Reserves implement rigorous anti-poaching measures to combat the illegal hunting and trade of elephant products. Strengthening law enforcement, enhancing surveillance systems, and increasing penalties for wildlife crimes are vital for protecting elephants.
Elephant Census and Monitoring Programs: Regular elephant census and monitoring programs are conducted to assess the population dynamics, distribution, and health of elephants in the reserves. This data helps in formulating conservation strategies and evaluating the effectiveness of conservation efforts.
Community-Based Conservation Projects: Engaging local communities in conservation initiatives is crucial for the long-term success of elephant conservation. Community-based projects focus on creating awareness, providing alternative livelihood options, and promoting sustainable practices that minimize conflicts and enhance coexistence between humans and elephants.
By addressing these challenges and implementing conservation initiatives, we can safeguard the future of elephants and their habitats, ensuring their ecological role and cultural significance for generations to come.
Conclusion
In conclusion, Elephant Reserves play a vital role in the conservation and protection of elephants in India. These reserves serve as crucial habitats for the survival of the Asian elephant, which is an iconic and endangered species. The establishment of Elephant Reserves, along with the implementation of various conservation initiatives, highlights the commitment of the Indian government and conservation organizations towards preserving these magnificent creatures and their habitats.
However, challenges such as habitat fragmentation, human-elephant conflict, and climate change continue to pose threats to the elephants and their ecosystems. It is essential to sustain efforts in habitat preservation, anti-poaching measures, community engagement, and international collaboration to ensure a brighter future for elephants in India.
By safeguarding these gentle giants and their natural habitats, we can contribute to overall biodiversity conservation and maintain the ecological balance for generations to come.
Thank You!
FAQs
How many elephant reserves in India in 2023?
India is home to 33 Elephant Reserves spread across different states. These Elephant Reserves are dedicated areas specifically designed for the conservation and protection of elephants and their habitats.
Which is the 33rd elephant reserve in India?
The 33rd Elephant Reserve established in India is known as the Terai Elephant Reserve, located in Uttar Pradesh. Covering an extensive area of 3,049 square kilometers.





