Teesta River: Map & Origin | India-Bangladesh
The Teesta River is a significant water body that originates in the Himalayas and flows through the Indian states of Sikkim and West Bengal before entering Bangladesh. With its rich geographical and environmental features, the river holds immense importance, not only as a natural resource but also as a key factor in regional politics and water management.
In this article, we will explore the various aspects of the Teesta River, including its origin, course, hydrology, ecological significance, and the ongoing water-sharing dispute between India and Bangladesh. Additionally, we’ll consider its relevance in the context of the India Map and the State.
| River | Teesta |
| Origin | Tso Lhamo Lake |
| Length | 414 Km |
| Elevation | 5,330 meters |
| Countries | India & Bangladesh |
Geographical Features of Teesta River
The Teesta River, located in the eastern part of the Indian subcontinent, possesses unique geographical features that contribute to its significance and impact on the region. Let’s delve into the origin and source of the river, its course, a map depicting its route, and the tributaries that enrich its flow.
- Originates from Tso Lhamo Lake in North Sikkim, India
- Flows through the Eastern Himalayas
- Forms a natural border between Sikkim and West Bengal states.
- The total length of approximately 414 kilometers.
- Features deep valleys, gorges, rapids, and waterfalls
- Offers opportunities for white-water rafting
- Receives contributions from tributaries such as Rangeet River, Rangpo River, Lachen Chu, and Lachung Chu.
Origin & Source
The Teesta River originates from the Tso Lhamo Lake in the North Sikkim district of the Indian state of Sikkim. Situated at an elevation of approximately 5,330 meters (17,490 feet), the glacial lake acts as the primary source of the river. The lake is fed by several glaciers, including the Zemu, Chumbi, and Lhonak glaciers, which receive abundant snowfall from the surrounding Himalayan peaks.
Course of Teesta
From its origin, the Teesta River traverses through the rugged terrain of the Eastern Himalayas, flowing in a generally southward direction. It forms a natural border between Sikkim and the Indian state of West Bengal.
The river meanders through deep valleys and gorges, carving its way through the mountainous landscape. As it descends, it forms numerous rapids and waterfalls, making it a popular destination for adventure enthusiasts seeking white-water rafting experiences. The river’s course exhibits stunning natural beauty, with breathtaking views of snow-capped peaks, dense forests, and picturesque villages along its banks.
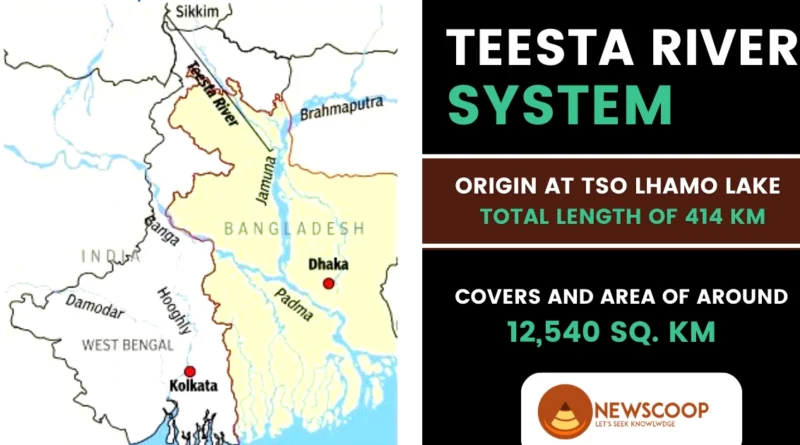
Map of Teesta River
Here is a map illustrating the course of the Teesta River:

The map showcases the journey of the Teesta River from its origin in North Sikkim, flowing through Sikkim and West Bengal, and finally merging with the Brahmaputra River in Bangladesh. The map highlights the major towns, cities, and geographical landmarks that the river passes through, providing a visual representation of its route.
Tributaries of Teesta River
The Teesta River is fed by several tributaries along its course. Here are some of the major tributaries of the Teesta River:
- Rangeet River
- Rangpo River
- Rongli River
- Lachen Chu
- Lachung Chu
- Dikchu River
Major Projects
The Teesta River has been used for different projects to generate electricity and support agriculture. Here are some important projects related to the Teesta River:
- Teesta-V Dam: This dam in Sikkim produces clean energy by using the flow of the River. It can generate 60 megawatts of electricity.
- Teesta Stage III and IV Hydropower Projects: These projects in Sikkim are being developed to generate electricity from the Teesta River. Stage III is expected to produce 1,200 megawatts, while Stage IV is expected to produce 520 megawatts.
- Teesta Low Dam Project: This project in West Bengal involves building a barrier across the Teesta River. It aims to use the river’s water for farming, controlling floods, and generating power.
- Teesta Barrage Project: Located in Bangladesh, this project controls the flow of this River. It includes building a barrier and canals to manage water for farming.
- Teesta River Basin Management Program: India and Bangladesh work together on this program to manage the water resources of the Teesta River. They share information and coordinate to use the river’s water efficiently.
India-Bangladesh Water Sharing Dispute
The water-sharing dispute between India and Bangladesh revolves around the equitable distribution of water from various rivers, including the Teesta River. This contentious issue has been a cause of concern between the two neighboring countries for several years. The primary point of contention is the allocation of water from the Teesta River. Bangladesh claims that it has not been receiving its fair share of water during the dry season, affecting its agriculture and overall water security.
Negotiations & Agreements
Establishment of the Joint River Commission (JRC) -1972: In 1972, India and Bangladesh established the Joint River Commission (JRC) as part of the Indo-Bangla Treaty of Friendship. The JRC aimed to facilitate discussions and cooperation on water-related issues, including the sharing of river waters.
Ad-Hoc Sharing Agreement for Teesta Water – 1983: In 1983, an agreement was reached for the ad-hoc sharing of Teesta River water between India and Bangladesh. This agreement was valid until the end of 1985 and provided a temporary framework for sharing the water resources of the Teesta River.
Revised in 1984: Revised Share for Bangladesh Based on the hydrological data assessed in 1984, the Joint River Commission (JRC) revised Bangladesh’s share of the Teesta River water, increasing its allocation. This adjustment was made to ensure a more equitable distribution of water resources between the two countries.
Bangladesh’s Teesta Barrage Project – 1998: In 1998, Bangladesh initiated the construction of the “Teesta Barrage” irrigation project. This project aimed to harness the waters of the Teesta River for irrigation purposes, allowing for three cropping seasons per year and enhancing agricultural productivity in the region.
Interim Water Sharing Deal – 2011: In 2011, an interim water sharing agreement was reached between India and Bangladesh regarding the Teesta River. This agreement was supposed to last for 15 years and allocated 42.5% of the Teesta water to India and 37.5% to Bangladesh. However, this agreement has not been implemented due to subsequent challenges and discussions.
What does Bangladesh want?
- Bangladesh wants a larger share of the Teesta River’s water.
- Specifically, it wants 50% of the Teesta’s waters from December to May.
- The aim is to protect the livelihoods of farmers and fishermen in Bangladesh.
- During the dry season, withdrawals of the Teesta’s waters in India cause water shortages in five districts of Bangladesh.
- These shortages have a significant impact on agriculture and the well-being of local communities.
- Bangladesh seeks a fair allocation to ensure water availability for irrigation and sustain agricultural productivity.
- Resolving the water-sharing dispute is essential through dialogue and cooperation between India and Bangladesh.
Importance for Bangladesh
The Teesta River’s floodplain covers approximately 14% of Bangladesh’s total cropped area. This fertile land provides vital agricultural opportunities for the country. The river’s waters are used for irrigation purposes, ensuring water availability for crops throughout the year. The River directly supports the livelihoods of approximately 73% of Bangladesh’s population, offering direct employment and income opportunities. Additionally, the river contributes to the fisheries sector, providing a source of food and income for local communities.
Importance for West-Bengal
The Teesta River is often referred to as the lifeline of North Bengal in the Indian state of West Bengal. Its waters are crucial for irrigation, supporting agricultural activities in the region. Nearly half a dozen districts in West Bengal, including Darjeeling, Jalpaiguri, and Cooch Behar, depend on the waters of the Teesta for agricultural production. The river plays a vital role in sustaining the agricultural economy and ensuring the water supply for various sectors in these districts.
Conclusion
The Teesta River, with its awe-inspiring geographical features, holds immense significance. Originating in the glacial realms of Sikkim and flowing through the Eastern Himalayas, it captivates with its stunning landscapes. The Rangeet River, Rangpo River, Lachen Chu, and Lachung Chu contribute to its hydrology.
Notably, projects like the Teesta-V Dam, Teesta Stage III and IV Hydropower Projects, Teesta Low Dam Project, and Teesta Barrage Project harness its water resources for power generation, irrigation, and water management. Balancing development with ecological preservation and equitable distribution, these initiatives shape the sustainable utilization of the Teesta River’s potential.
Thank You!
Where does the Teesta River originate?
The Teesta River originates from Tso Lhamo Lake in North Sikkim, India.
What is the total length of the Teesta River?
The Teesta River has a total length of approximately 414 kilometers.
Related links: